Measure Sound Better
What Is a Data Acquisition System? DAQ Types, Key Specs & Selection Guide
Table of content
A complete engineer’s guide to DAQ systems: PCIe/PXI cards, USB/Ethernet recorders, modular multi-channel systems. Covers dynamic range, PTP sync, IEPE, and how to select the right DAQ for NVH, vibration & acoustic testing.
A data acquisition system (DAQ) is the measurement front end: it converts analog sensor outputs—such as voltage, current, and charge—into digital data. The signal is first conditioned (amplification, filtering, isolation, IEPE excitation, etc.) and then fed to an ADC, where it is digitized at the specified sampling rate and resolution; software subsequently handles visualization, storage, and analysis. This article systematically reviews common DAQ form factors, including PCIe/PXI plug-in cards, external USB/Ethernet/Thunderbolt devices, integrated data recorders, and modular distributed systems. It also summarizes key selection criteria—signal compatibility, channel headroom and scalability, sampling rate and anti-aliasing filtering, dynamic range, THD+N, clock synchronization and inter-channel delay, as well as delivery and after-sales support—to help readers quickly build a clear understanding of DAQ systems.
Why Data Acquisition Matters?
In the real world, physical stimuli such as temperature, sound, and vibration are everywhere. We can sense them directly; in a sense, the human body itself is a “data acquisition system”: our senses act like sensors that capture signals, the nervous system handles transmission and encoding, the brain fuses and analyzes the information to make decisions, and muscles execute actions—forming a closed feedback loop.
Progress in science and engineering ultimately comes from observing, understanding, and validating the world with more reliable methods. Physical quantities such as temperature, sound pressure, vibration, stress, and voltage are the primary carriers of information. However, human perception is subjective and cannot quantify these changes accurately and repeatably; and in high-current, high-temperature, high-stress, or high-SPL environments, direct exposure can even cause irreversible harm. To enable measurement that is quantifiable, recordable, and safer, data acquisition systems (DAQ) came into being.

Put simply, a data acquisition system (DAQ) is an analog front end that converts a sensor's analog output (voltage/current/charge, etc.) into digital data at a defined sampling rate and resolution, and hands it to software for display, logging, and analysis (typically with the required signal conditioning). It helps engineers see problems more clearly—and solve them.
In today's development cycles—from cars and aircraft to consumer electronics—it's difficult to validate performance, safety, and reliability efficiently without data acquisition. In durability testing, DAQ records cyclic load and strain for fatigue-life analysis; in noise control, synchronous multi-point acquisition of vibration and sound pressure helps identify noise sources and transmission paths. This quantitative capability is what provides a scientific basis for engineering improvements.
DAQ applications span a wide range of fields:
- Automotive NVH and mechanical vibration testing: Used to acquire body vibration, noise, engine balance, structural modal data, and more—helping engineers improve vehicle ride comfort.
- Audio testing: In the development and production of speakers, microphones, headphones, and other audio devices, DAQ is used to measure frequency response, SPL, distortion, and more, to verify acoustic performance.
- Industrial automation and monitoring: DAQ is widely used for process monitoring, condition monitoring, and industrial control. For example, it acquires temperature, pressure, flow, and torque sensor signals to enable real-time monitoring and alarms, and it often must run continuously with high stability and strong immunity to interference.
- Research labs and education: From physics and biology experiments to seismic monitoring and weather observation, DAQ is a basic tool for capturing raw data. It makes data recording automated and digital, which simplifies downstream processing.
As quality and performance requirements continue to rise across industries, DAQ has become an indispensable set of “eyes and ears,” giving engineers the ability to observe and interpret complex phenomena.
Common DAQ Form Factors
Depending on interface, level of integration, and the application, DAQ hardware comes in several common forms. Below are a few typical DAQ card/system categories:
| Type | Form factor / Interface | Advantages | Limitations | Typical Application |
| Plug-in DAQ card | PCIe / PXI / PXIe | Low latency; high throughput; strong real-time performance | Not portable; requires chassis/industrial PC; expansion limited by platform | Fixed labs; rack systems; high-throughput acquisition |
| External DAQ device | USB / Ethernet / Thunderbolt | Portable; fast setup; laptop-friendly | Bandwidth/latency depends on interface; driver stability is critical; mind power and cabling | Field testing; mobile measurements; general-purpose DAQ |
| Integrated data recorder | Built-in battery/storage/display (standalone) | Ready out of the box; easy in the field; straightforward offline logging | Channel count/algorithms often limited; weaker expandability; post-processing depends on export | Patrol inspection; quick diagnostics; long-duration offline logging |
| Modular distributed system | Mainframe + modules; network expansion (synchronized) | Mix signal types as needed; easy channel scaling; strong synchronization | Planning matters: sync/clock/cabling; system design becomes more important at scale | Synchronized Multi-Physics Measurement;High-Channel-Count Scalability;Distributed, Multi-Site Testing |
- Plug-in DAQ cards (internal): These are boards installed inside a computer, with typical interfaces such as PCI, PCIe, and PXI (CompactPCI). They plug directly into the PC/chassis bus and are powered and controlled by the host, providing high bandwidth and strong real-time performance for high-throughput applications in desktop or industrial PC environments. The trade-off is portability—these are usually used in fixed labs or rack systems.

- External DAQ devices (modules): DAQ hardware that connects to a computer via USB, Ethernet, Thunderbolt, and similar interfaces. USB DAQ is common—compact, plug-and-play, and well-suited to laptops and field testing. Ethernet/network DAQ enables longer cable runs and multi-device connections. External units are generally portable with their own enclosure, but high-end models may be somewhat limited in real-time performance by interface bandwidth (USB latency is typically higher than PCIe).

- Portable / integrated data recorders: These integrate the DAQ hardware with an embedded computer, display, and storage to form a standalone instrument. They're convenient in the field and can acquire, log, and do basic analysis without an external PC. Examples include portable vibration acquisition/analyzer units with tablet-style displays and handheld multi-channel recorders. They are typically optimized for specific applications, ready to use out of the box, and well-suited for mobile measurements or quick on-site diagnostics.
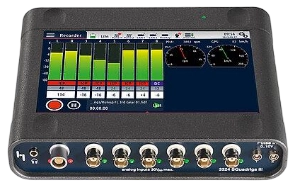
- Modular distributed DAQ system platform: Built from multiple acquisition modules and a main controller/chassis, allowing flexible channel scaling and mixing of different function modules. Each module handles a certain signal type or channel count and connects to the controller (or directly to a PC) over a high-speed, time-synchronized network (e.g., EtherCAT, Ethernet/PTP). This architecture offers very high scalability and distributed measurement capability; modules can be placed close to the test article to reduce sensor cabling. For example, CRYSOUND's SonoDAQ is a modular platform: each mainframe supports multiple modules and can be expanded via daisy-chain or star topology to thousands of channels. Modular systems are a strong fit for large-scale, cross-area synchronized measurement.

What Makes Up a DAQ System?
A complete data acquisition system typically includes the following key building blocks:
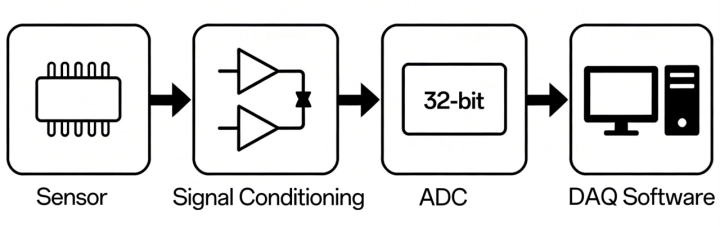
- Sensors: The front end that converts physical phenomena into electrical signals—for example, microphones that convert sound pressure to voltage, accelerometers that convert acceleration to charge/voltage, strain gauges that convert force to resistance change, and thermocouples for temperature measurement;
- Signal conditioning: Electronics between the sensor and the DAQ ADC that adapts and optimizes the signal.Typical functions include gain/attenuation (scaling signal amplitude into the ADC input range), filtering (e.g., anti-aliasing low-pass filtering to remove noise/high-frequency content), isolation (signal/power isolation for noise reduction and protection), and sensor excitation (providing power to active sensors, such as constant-current sources for IEPE sensors).
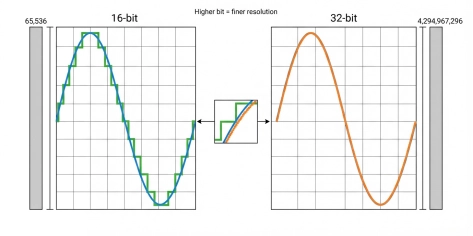
- Analog-to-digital converter (ADC): The core component that converts continuous analog signals into discrete digital samples at the configured sampling rate and resolution. Sampling rate sets the usable bandwidth (it must satisfy Nyquist and include margin for the anti-aliasing filter transition band), while resolution (bit depth) affects quantization step size and usable dynamic range. Many DAQ products use 16-bit or 24-bit ADCs; in high-dynamic-range acoustic/vibration front ends (such as platforms like SonoDAQ), you may also see 32-bit data output/processing paths to better cover wide ranges and weak signals (depending on the specific implementation and how the specs are defined).
- Data interface and storage: The ADC's digital data must be delivered to a computer or storage media. Plug-in DAQ writes directly into host memory over the system bus. USB/Ethernet DAQ streams data to PC software through a driver. In addition to USB/Ethernet/wireless data transfer, SonoDAQ also supports real-time logging to an onboard SD card, allowing standalone recording without a PC—useful as protection against link interruptions or for long-duration unattended acquisition.
- Host PC and software: This is the back end of a DAQ system. Most modern DAQ relies on a computer and software for visualization, logging, and analysis. Acquisition software sets sampling parameters, controls the measurement, displays waveforms in real time, and processes data for results and reporting. Different vendors provide their own platforms (e.g., OpenTest, NI LabVIEW/DAQmx, DewesoftX, HBK BK Connect). Software usability and capability directly impact productivity. In addition, CRYSOUND's OpenTest supports protocols such as openDAQ and ASIO, enabling configuration with multiple DAQ systems.
What Specs Matter When Selecting a DAQ?
Three common selection pitfalls:
- Focusing only on “sampling rate / bit depth” while ignoring front-end noise, range matching, anti-aliasing filtering, and synchronization metrics: the data may “look like it's there,” but the analysis is unstable and not repeatable.
- Sizing channel count to “just enough” with no headroom: once you add measurement points, you're forced to replace the whole system or stack a second system—increasing cost and integration effort.
- Focusing only on hardware while ignoring software and workflow: configuration, real-time monitoring, batch testing, report export, and protocol compatibility (openDAQ/ASIO, etc.) directly determine throughput.
What you should evaluate:
- Signal types to acquire: In selection, clearly defining your signal types is the first step. Acoustic/vibration measurements are very different from stress, temperature, and voltage measurements. Traditional systems often support only a subset of signal types—for example, only sound pressure and acceleration—so when the requirement expands to temperature, you may need a second system, which increases budget and adds integration/synchronization complexity. SonoDAQ uses a modular platform approach: by inserting the required signal-type modules, you can expand capability within one system and run synchronized multi-physics tests—configuring what you need in one platform.
- Channel count and scalability: First determine how many signals you need to acquire and choose a DAQ with enough analog input channels (or a system that can expand). It's best to leave some margin for future points—for example, if you need 12 channels today, consider 16+ channels. Equally important is scalability: SonoDAQ can be synchronized across multiple units to scale to hundreds or even thousands of channels while maintaining inter-channel acquisition skew < 100 ns, which suits large-scale testing. By contrast, fixed-channel devices cannot be expanded once you exceed capacity, forcing a replacement and increasing cost.

- Match sampling rate to signal bandwidth: start with the highest frequency/bandwidth of interest. The baseline is Nyquist (sampling rate > 2× the highest frequency). In practice, you also need margin for the anti-aliasing filter transition band, so many projects start at 2.5–5× bandwidth and then fine-tune based on the analysis method (FFT, octave bands, order tracking, etc.). For example, if engine vibration content tops out at 1 kHz, you might start at 5.12 kS/s or higher; for speech/acoustics that needs to cover 20 kHz, common choices are 51.2 kS/s or 96 kS/s. In short: base it on the spectrum, keep some margin, and align it with your filtering and analysis.
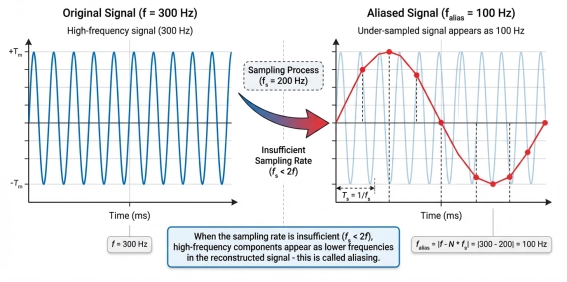
- Measurement accuracy and dynamic range: If your application needs to resolve weak signals while also covering large signal swings—for example, NVH tests often need to capture very low noise in quiet conditions and also record high SPL under strong excitation—you need a high-dynamic-range, high-resolution DAQ (24-bit ADC or higher, dynamic range > 120 dB). For audio testing, where distortion and noise floor matter and you want the DAQ's self-noise to be well below the DUT, choose a low-noise, high-SNR front end and check vendor specs such as THD+N.
- Environment and use constraints: Think about where the DAQ will be used: on a lab bench, on the factory floor, or outdoors in the field. If you need to travel frequently or test on a vehicle, a portable/rugged DAQ is usually a better fit.For scenarios without stable power for long periods, built-in battery capability and battery runtime become critical.

- Lead time and after-sales support: After you define the procurement need, delivery lead time is a practical factor you can't ignore. If your schedule is tight, a 2–3 month lead time can directly delay project kickoff and execution, so evaluate the supplier's delivery commitment. Support is equally important: training, responsiveness when issues occur, and whether remote or on-site assistance is available. Also review warranty terms, software upgrade policy, and support response mechanisms—these directly affect long-term system stability and overall project efficiency.

With the above steps, you can narrow down the DAQ characteristics that fit your application and make a defensible choice from a crowded product list. In short: start from requirements, focus on the key specs, plan for future expansion, and don't ignore vendor maturity and support. Choose the right tool, and testing becomes far more efficient.
FAQ
Q: Can I use a sound card as a DAQ?
A: For a small number of audio channels where synchronization/range/calibration requirements are not strict, a sound card can “work” at a basic level. But in engineering test work, common issues are: no IEPE excitation, insufficient input range and noise floor, uncontrolled channel-to-channel sync, and driver latency that is high and unstable. If you need repeatable, traceable test data, use a professional DAQ front end.
Q: What's the difference between a DAQ and an oscilloscope?
A: An oscilloscope is more of an electronics debugging tool—great for capturing transients and doing quick troubleshooting. A DAQ is more of a long-duration, multi-channel, time-synchronized acquisition and analysis system, with an emphasis on channel scalability, synchronization consistency, long-term stability, and data management.
Q: How do I choose the sampling rate?
A: Start from the highest frequency/bandwidth of interest and meet Nyquist (>2× fmax) as a baseline. In practice, also account for the anti-aliasing filter transition band and your analysis method; starting at 2.5–5× bandwidth is usually safer. If you're unsure, prioritize proper filtering and dynamic range first, then optimize sampling rate.
Q: What is IEPE, and when do I need it?
A: IEPE is a constant-current excitation scheme used by sensors such as accelerometers and IEPE measurement microphones, with power and signal on the same cable. If you use IEPE sensors, your DAQ front end must support IEPE excitation, appropriate isolation/grounding strategy, and suitable input range and bandwidth.
Q: What should I check for multi-channel / multi-device synchronization?
A: Focus on three things: a common clock source (external clock/PTP/GPS, etc.), channel-to-channel sampling skew/delay, and trigger/alignment strategy. For NVH, array measurements, and structural modal testing, sync performance often matters more than single-channel specs.
Q: How do I estimate channel count—and should I leave headroom?
A: List the “must-measure” signals and points first, then add auxiliary channels such as tach/trigger/temperature. A good rule is to reserve at least 20%–30% headroom, or choose a modular platform that scales, so you're not forced to replace the system when points get added.
If you'd like to learn more about the latest intelligent sound & vibration data acquisition system, SonoDAQ, from CRYSOUND, including its key features, typical application scenarios, and common configuration options, please fill out the Get in touch form below to contact the CRYSOUND team.
You're also welcome to reach out to the CRYSOUND team. Based on your constraints—such as signal types, channel count, sampling rate/bandwidth, synchronization requirements, and on-site environmental conditions—we can provide a product demo and practical configuration recommendations.
Related Products
SonoDAQ Pro
OpenTest
CRY3213 NVH Measurement Microphone






Get in touch
If you are interested or have questions about our products, book a demo and we will be glad to show how it works, which solutions it can take part of and discuss how it might fit your needs and organization.


.112_结果_结果_2-scaled-3-300x208.webp)