December 16, 2025
Abnormal Noise Detection: From Human Ears to AI
With the rapid growth of consumer audio products such as headphones, loudspeakers and wearables, users’ expectations for “good sound” have moved far beyond simply being able to hear clearly. Now they want sound that is comfortable, clean, and free from any extra rustling, clicking or scratching noises.
However, in most factories, abnormal noise testing still relies heavily on human listening. Shift schedules, subjective differences between operators, fatigue and emotional state all directly impact your yield rate and brand reputation.
In this article, based on CRYSOUND’s real project experience with AI listening inspection for TWS earbuds, we’ll talk about how to use AI to “free human ears” from the production line and make listening tests truly stable, efficient and repeatable.
Why Is Audio Listening Test So Labor-Intensive?
In traditional setups, the production line usually follows this pattern:
automatic electro-acoustic test + manual listening recheck.
The pain points of manual listening are very clear:
- Strong subjectivity: Different listeners have different sensitivity to noises such as “rustling” or “scratching”. Even the same person may judge inconsistently between morning and night shifts.
- Poor scalability: Human listening requires intense concentration, and it’s easy to become fatigued over long periods. It’s hard to support high UPH in mass production.
- High training cost: A qualified listener needs systematic training and long-term experience accumulation, and it takes time for new operators to get up to speed.
- Results hard to trace: Subjective judgments are difficult to turn into quantitative data and history, which makes later quality analysis and improvement more challenging.
That’s why the industry has long been looking for a way to use automation and algorithms to handle this work more stably and economically—without sacrificing the sensitivity of the “human ear.”
From “Human Ears” to “AI Ears”: CRYSOUND’s Overall Approach
CRYSOUND’s answer is a standardized test platform built around the CRYSOUND abnormal noise test system, combined with AI listening algorithms and dedicated fixtures to form a complete, integrated hardware–software solution.
Key Characteristics of the Solution:
- Standardized, multi-purpose platform: Modular design that supports both conventional SPK audio / noise tests and abnormal noise / AI listening tests.
- 1-to-2 parallel testing: A single system can test two earbuds at the same time. In typical projects, UPH can reach about 120 pcs.
- AI listening analysis module: By collecting good-unit data to build a model, the system automatically identifies units with abnormal noise, significantly reducing manual listening stations.
- Low-noise test environment: A high-performance acoustic chamber plus an inner-box structure control the background noise to around 12 dBA, providing a stable acoustic environment for the AI algorithm.
In simple terms, the solution is:
One standardized test bench + one dedicated fixture + one AI listening algorithm.

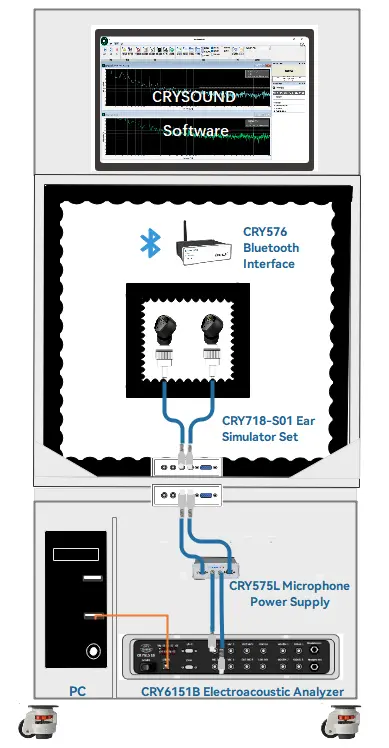
Typical Test Signal Path
Centered on the test host, the “lab + production line” unified chain looks like this:
- PC host → CRY576 Bluetooth Adapter → TWS earphones
- Earphones output sound, captured by CRY718-S01 Ear Simulator
- Signal is acquired and analyzed by the CRY6151B Electroacoustic Analyzer
- The software calls the AI listening algorithm module, performs automatic analysis on the WAV data and outputs a PASS/FAIL result
Fixtures and Acoustic Chamber: Minimizing Station-to-Station Variation
Product placement posture and coupling conditions often determine test consistency. The solution reduces test variation through fixture and chamber design to fix the test conditions as much as possible:
- Fixture: Soft rubber shaped recess.
- The shaped recess ensures that the earbud is always placed against the artificial ear in the same posture, reducing position errors and test variation.
- The soft rubber improves sealing and prevents mechanical damage to the earphones.
- Acoustic box: Inner-box damping and acoustic isolation.
- This reduces the impact of external mechanical vibration and environmental noise on the measurement results.
Professional-Grade Acoustic Hardware (Example Configuration)
CRY6151B Electroacoustic Analyzer
- Frequency range 20–20 kHz, low background noise and high dynamic range, integrating both signal output and measurement input.
CRY718-S01 Ear Simulator Set
- Meets relevant IEC / ITU requirements. Under appropriate configurations / conditions, the system’s own noise can reach the 12 dBA level.
CRY725D Shielded Acoustic Chamber
- Integrates RF shielding and acoustic isolation, tailored for TWS test scenarios.
AI Algorithm: How Unsupervised Anomaly Detection “Recognizes the Abnormal”
Training Flow: Only “Good” Earphones Are Needed
CRYSOUND’s AI listening solution uses an unsupervised anomalous sound detection algorithm. Its biggest advantage is that it does not require collecting many abnormal samples in advance—only normal, good units are needed to train a model that “understands good sound”.
In real projects, the typical steps are as follows:
- Prepare no fewer than 100 good units. Under the same conditions as mass production testing, collect WAV data from these 100 units.
- Train the model using these good-unit data (for example, 100 samples of 10 seconds each; training usually takes less than 1 minute).
- Use the model to test both good and defective samples, compare the distribution of the results, and set the decision threshold.
- After training, the model can be used directly in mass production. Prediction time for a single sample is under 0.5 seconds.
In this process, engineers do not need to manually label each type of abnormal noise, which greatly lowers the barrier to introducing the system into a new project.
Principle in Brief: Let the Model “Retell” a Normal Sound First
Roughly speaking, the algorithm works in three steps:
Time-frequency conversion
- Convert the recorded waveform into a time-frequency spectrogram (like a “picture of the sound”).
Deep-learning-based reconstruction
- Use the deep learning model trained on “normal earphones” to reconstruct the time-frequency spectrogram.
- For normal samples, the model can more or less “reproduce” the original spectrogram. For samples containing abnormal noise, the abnormal parts are difficult to reconstruct.
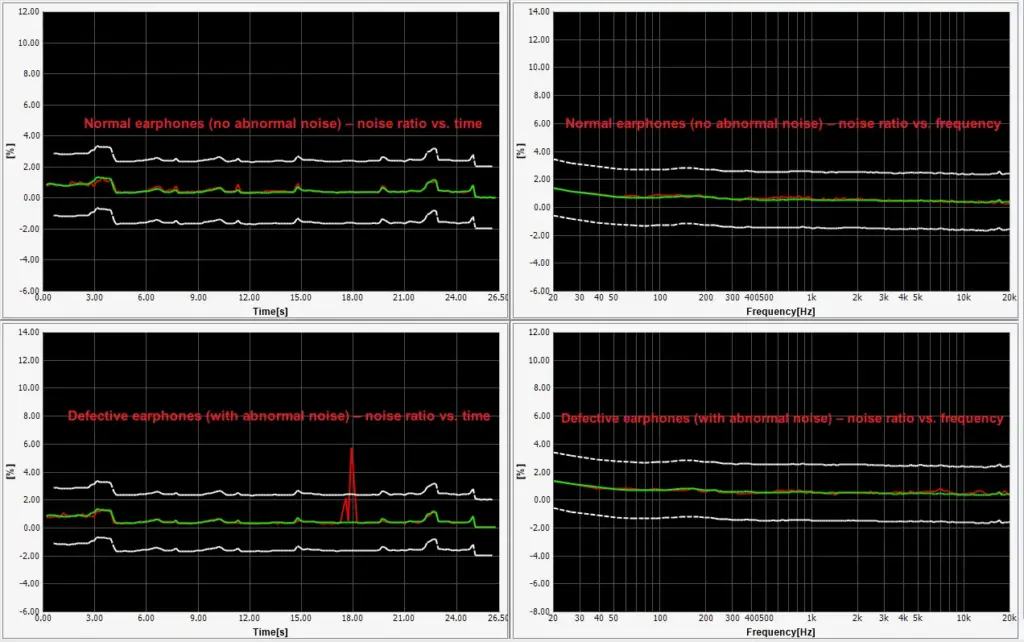
Difference analysis
- Compare the original spectrogram with the reconstructed one and calculate the difference along the time and frequency axes to obtain two difference curves.
- Abnormal samples will show prominent peaks or concentrated energy areas on these curves.
In this way, the algorithm develops a strong fit to the “normal” pattern and becomes naturally sensitive to any deviation from that pattern, without needing to build a separate model for each type of abnormal noise.
In actual projects, this algorithm has already been verified in more than 10 different projects, achieving a defect detection rate of up to 99.9%.
Practical Advantages of AI Listening
- No dependence on abnormal samples: No need to spend enormous effort collecting various “scratching” or “electrical” noise examples.
- Adapts to new abnormalities: Even if a new type of abnormal sound appears that was not present during training, as long as it is significantly different from the normal pattern, the algorithm can still detect it.
- Continuous learning: New good-unit data can be continuously added later so that the model can adapt to small drifts in the line and environment over the long term.
- Greatly reduced manual workload: Instead of “everyone listening,” you move to “AI scanning + small-batch sampling inspection,” freeing people to focus on higher-value analysis and optimization work.
A Typical Deployment Case: Real-World Practice on an ODM TWS Production Line
On one ODM’s TWS production line, the daily output per line is on the order of thousands of sets. In order to improve yield and reduce the burden of manual listening, they introduced the AI abnormal-noise test solution:
| Item | Before Introducing the AI Abnormal-Noise Test Solution | After Introducing the AI Abnormal-Noise Test Solution |
| Test method | 4 manual listening stations, abnormal noises judged purely by human listeners | 4 AI listening test systems, each testing one pair of earbuds |
| Manpower configuration | 4 operators (full-time listening) | 2 operators (for loading/unloading + rechecking abnormal units) |
| Quality risk | Missed defects and escapes due to subjectivity and fatigue | During pilot runs, AI system results matched manual sampling; stability improved significantly |
| Work during pilot stage | Define manual listening procedures | Collect samples, train the AI model, set thresholds, and validate feasibility via manual sampling |
| Daily line capacity (per line) | Limited by the pace of manual testing | About 1,000 pairs of earbuds per day |
| Abnormal-noise detection rate | Missed defects existed, not quantified | ≈ 99.9% |
| False-fail rate (good units misjudged) | Affected by subjectivity and fatigue, not quantified | ≈ 0.2% |
On this line, AI listening has essentially taken over the original manual listening tasks. Not only has the headcount been cut by half, but the risk of missed defects has been significantly reduced, providing data support for scaling the solution across more production lines in the future.
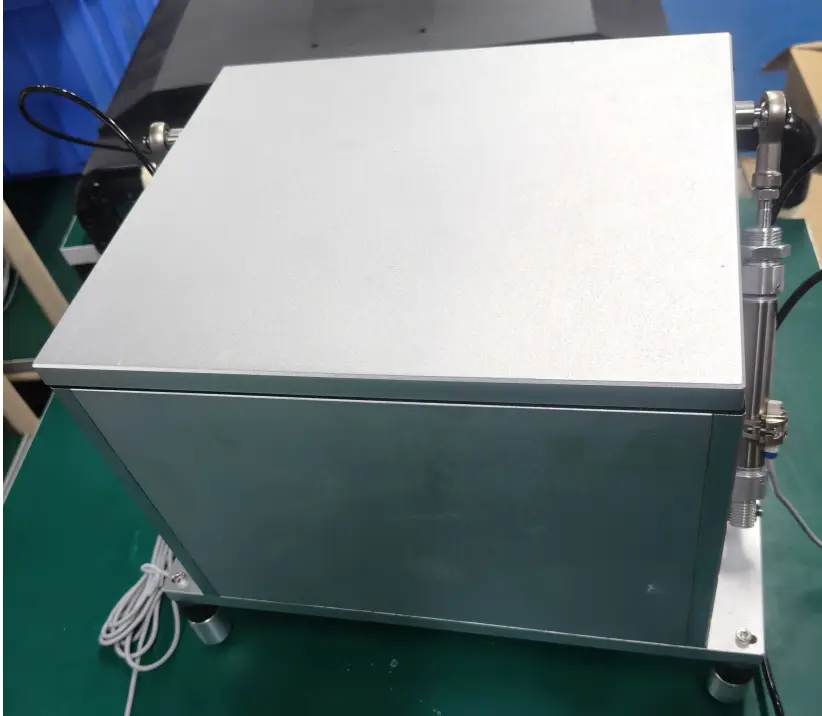
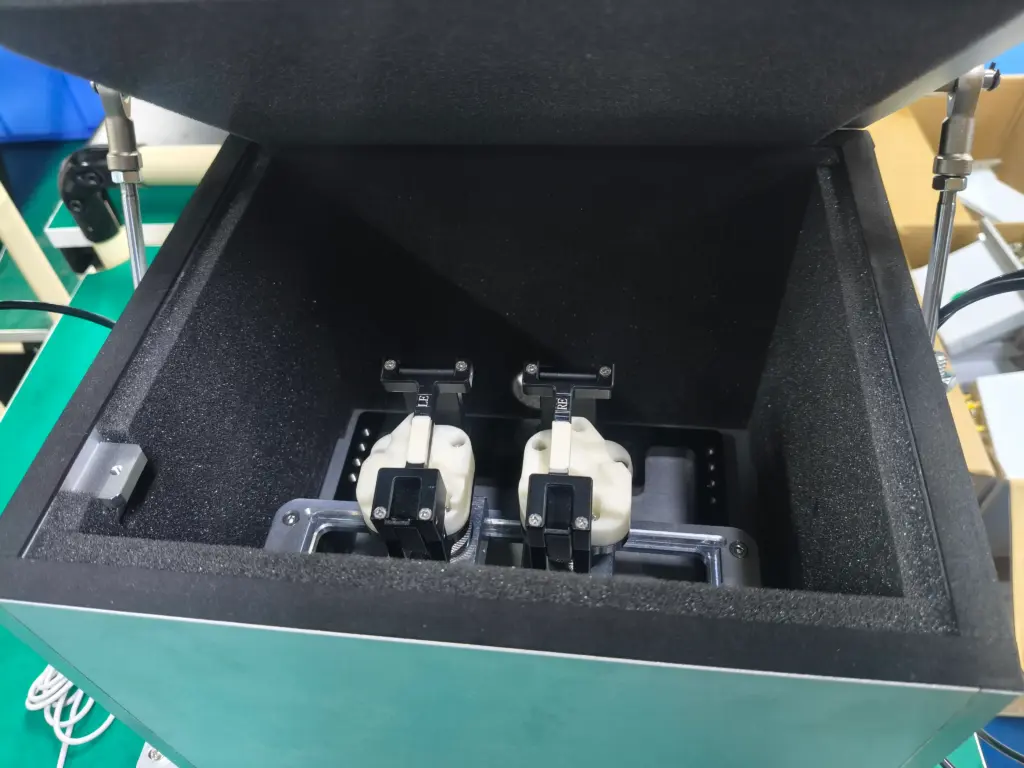


Deployment Recommendations: How to Get the Most Out of This Solution
If you are considering introducing AI-based abnormal-noise testing, you can start from the following aspects:
Plan sample collection as early as possible
- Begin accumulating“confirmed no abnormal-noise”good-unit waveforms during the trial build /small pilot stage, so you can get a head start on AI training later.
Minimize environmental interference
- The AI listening test station should be placed away from high-noise equipment such as dispensing machines and soldering machines.
- By turning off alarm buzzers, defining material-handling aisles that avoid the test stations, and reducing floor vibration, you can effectively lower false-detection rates.
Keep test conditions consistent
- Use the same isolation chamber, artificial ear, fixtures and test sequence in both the training and mass-production phases, to avoid model transfer issues caused by environmental differences.
Maintain a period of human–machine coexistence
- In the early stage, you can adopt a“100% AI + manual sampling”strategy, and then gradually transition to“100% AI + a small amount of DOA recheck,”in order to minimize the risks associated with deployment.
Conclusion: Let Testing Return to “Looking at Data” and Put People Where They Create More Value
AI listening tests, at their core, are an industrial upgrade—from experience-based human listening to data- and algorithm-driven testing.
With standardized CRYSOUND test platforms, professional acoustic hardware, product-specific fixtures and AI algorithms, CRYSOUND is helping more and more customers transform time-consuming, labor-intensive and subjective manual listening into something stable, quantifiable and reusable.
If you’d like to learn more about abnormal-noise testing for earphones, or planning to try AI listening on your next-generation production line—or discuss your blade process and inspection targets—please use the “Get in touch” form below. Our team can share recommended settings and an on-site workflow tailored to your production conditions.

